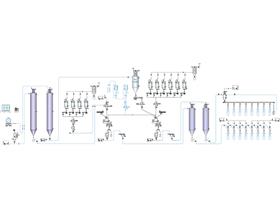
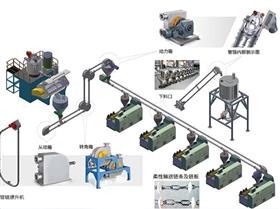
Everything You Need to Know About Pneumatic Conveying Equipment
Pneumatic Conveying Equipment uses air or gas to move bulk materials. Many industries use this technology for powders or granules. Some examples are:
- Food processing
- Pharmaceuticals
- Cement
- Steel
- Chemicals
These systems help move materials fast, safely, and easily in your facility.
Key Takeaways
- Pneumatic conveying systems use air to move materials fast and safely. These systems work well in food and medicine factories.
- Picking the right blower and feeder is very important. Good choices help save energy and lower repair costs.
- Knowing about the material size and how rough it is helps you choose the best system. This makes sure the pneumatic conveying system fits your needs.
- Regular care keeps your pneumatic conveying equipment working well. Check and clean your system often to stop problems.
- Do not make mistakes like ignoring material size or bad system design. Good planning helps your system work better and have fewer problems.
How Pneumatic Conveying Works
Basic Operation Principle
You use Pneumatic Conveying Equipment to move bulk materials in pipes with air or gas. The system makes an air flow that pushes or pulls powders and granules from one place to another. You do not need belts or chains for this. The moving air does all the work. This way, materials stay inside the pipes. It helps stop spills and keeps things clean. You can move many types of materials, like fine powders or bigger granules. The system is good for industries that want clean and fast transport.
Tip: You can change the system to fit your material and process. This makes Pneumatic Conveying Equipment a top choice for many industries.
Airflow and Material Transport
Airflow is what moves materials in pneumatic conveying. You control the air speed and pressure for each material. Different materials need different air speeds to move well and not get stuck. The table below shows common airflow speeds for some materials:
Material | Airflow Velocity (m/s) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
Cement | 10 - 11 | Needs a lower speed because of a bigger surface area. |
Fly Ash | 11 - 12 | Needs a higher speed because it is round. |
Granular Sugar | 16 | Needs higher speed because pieces are similar in size. |
Fine/Granular Particles | 13 - 15 | Needs higher speeds to move well. |
You must think about the size and weight of your material. These things change how well the system works. Here are some key points:
- The kind of material, like particle size and bulk weight, is important when you pick a pneumatic conveying system.
- Materials have different traits like moisture, how rough they are, if they break easily, and if they are toxic. These things change how easy it is to move them.
- You need to match the system to your material to stop problems like clogging or damage.
Common Applications
You see Pneumatic Conveying Equipment in many industries. You can use it to move food, chemicals, cement, and even medicine powders. The system is good for dangerous or sensitive materials because it keeps everything inside. This design keeps your product and workers safe.
Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
Seamless Material Transfer | Closed pipes stop spills and keep things clean and safe. |
Flexibility and Versatility | You can change the system to move materials in many ways. |
Increased Efficiency and Productivity | Machines do the work, so people do not have to, which saves time and helps work go faster. |
Dust-Free Operation | The system does not make dust, which is good for product quality and worker health. |
Cost-Effective Solution | You save money over time because you need less fixing and use less energy. |
You can use these systems for loading silos, feeding mixers, or moving powders between steps. You get a cleaner workspace and better control of your materials. You also make things safer and spend less on repairs.
Key Components of Pneumatic Conveying Equipment
When you build or use a pneumatic conveying system, you need to know its main parts. Each part helps move materials safely and quickly. Let's look at the most important pieces in Pneumatic Conveying Equipment.
Blowers and Compressors
Blowers and compressors make the airflow that moves your materials. The blower you pick changes how much energy your system uses. It also affects how well your system works. Here is a table that shows the most common blower types and what they do:
Type of Blower | Description |
|---|---|
Forward-curved blades | Designed for high airflow and low-pressure applications. |
Backward-curved blades | More efficient at higher pressures, suitable for various industrial uses. |
Radial blades | Provide high pressure and are used in applications requiring strong airflow. |
Airfoil blades | Offer high efficiency and are used in specialized applications. |
You see these blowers in places like cement and mining. For example, you use them for moving raw materials, collecting dust, and helping air flow. When you pick a blower, think about how much energy it uses. Airfoil bearing turbo blowers can save up to 30% more energy than older blowers. These blowers use special motors and direct-drive systems. This helps stop energy loss. You also get better control and less friction. Your system runs smoothly and costs less to use.
Tip: Picking the right blower or compressor can help you save money on energy and make your system last longer.
Feeders and Entry Points
Feeders and entry points control how materials go into the system. You need a steady flow to stop blockages and keep things moving. Common feeders are screw feeders, rotary valves, and vibratory feeders. You pick the feeder based on your material's size, shape, and how it flows. If you move powders, you want a feeder that stops clumping and keeps the powder moving. Entry points must seal tightly to stop air leaks and keep the pressure steady.
Ducts and Pipelines
Ducts and pipelines are the path for your materials. You use strong, smooth pipes to move powders and granules. The size and shape of the pipes change how fast and well your materials travel. You want to avoid sharp bends and sudden pipe changes. These can cause blockages or wear out your system faster. You should pick pipe materials that match what you move. For example, tough pipes are best for rough materials.
Receivers and Separators
Receivers and separators collect your materials at the end. They also separate the air from the solids. You often use cyclone separators, bag filters, or dust collectors for this job. These devices make sure only clean air leaves the system. This keeps your workspace and the environment safe. Good receivers and separators help you keep almost all your product. You waste less and keep your process working well.
Valves and Airlocks
Valves and airlocks control the flow of materials and keep the system sealed. Rotary airlock valves are the most common type. You use them to let materials in and out without losing air pressure. These valves keep the system airtight. This stops leaks and keeps your process safe. They work well with powders, granules, and bulk solids. The design of your airlock matters. Strong construction and careful building make sure the valve works well, even when things get tough. Good airlocks also help your dust collection system work better and keep your plant safe.
Note: Good valves and airlocks are important for keeping your system working well and stopping material loss.
When you know these key parts, you can build or keep a pneumatic conveying system that works smoothly, saves energy, and keeps your materials safe.
Types of Pneumatic Conveying Systems
Dilute Phase Conveying
Dilute phase conveying moves light materials that flow easily. The system uses fast air to keep materials floating in the pipes. You see this system in food, plastics, chemicals, medicine, and farming. It works best for products that are not rough and do not break.
Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|
Fast air keeps materials moving | Food processing |
Materials stay floating in the pipes | Plastics |
Good for light, smooth, flowing items | Chemicals |
| Pharmaceuticals |
| Agriculture |
This system is easy to set up and costs less to install. But fast air can wear out pipes and parts, so you may fix things more often.
Dense Phase Conveying
Dense phase conveying moves materials slowly and uses more material with less air. You use it for items that break or scratch easily. This system helps stop damage and saves energy. Dense phase is good for grains, minerals, and powders that can break or wear down machines.
Feature | Dense Phase Conveying | Dilute Phase Conveying |
|---|---|---|
Moves slower | Lower velocities | Higher velocities |
Uses more material, less air | Higher loading ratios | Lower loading ratios |
Saves energy | Less energy consumption | Higher energy consumption |
Handles fragile items | Suitable for fragile/abrasive | Can lead to degradation |
Needs less fixing | Lower maintenance needs | Higher maintenance |
You pay more to set up dense phase, but you save money on repairs and energy later.
Vacuum Conveying
Vacuum conveying pulls materials with an air pressure that is lower than normal. You use it for fine powders and items that break easily. Vacuum systems keep your workspace clean and safe. They fit in small spaces and work with old lines.
- You work in a closed space, so things stay clean.
- You stop dust from getting out and keep workers safe.
- You need less room than other systems.
- You can move many kinds of materials and add this system to what you have.
- You fix things less because there are fewer moving parts.
- You use less energy and spend less money.
System Comparison
You need to pick the right system for your materials and how you work. Each system costs different amounts and needs different care.
System Type | Installation Cost | Maintenance Requirements |
|---|---|---|
Dilute Phase | Low | High |
Dense Phase | High | Low |
The dilute phase is good for simple jobs and easy-to-move items. Dense phase is better for tough, breakable, or rough products. Vacuum conveying is best for clean, safe, and flexible moving of powders and gentle items.
Tip: Pick your Pneumatic Conveying Equipment based on your material and how your space is set up. This helps you work better and save money.
Selecting Pneumatic Conveying Equipment
Material Properties
You need to think about your material before picking a system. Each property changes how the equipment works with your product. The table below lists the main things to check:
Material Property | Description |
|---|---|
Bulk Density | Changes how heavy and big the material is. |
Particle Size | Changes how well it moves and how you move it. |
Particle Shape | Changes how materials touch each other and the system. |
Abrasiveness | Changes how much the equipment wears out. |
Fragility | Changes how likely the material break while moving. |
Dustiness | Changes sin afety and the environment. |
Cohesiveness | Changes how materials stick and move together. |
Hygroscopicity | Changes how much moisture the material takes in. |
You should match your system to these things. This helps stop clogs, lowers damage, and keeps things working well.
Distance and Layout
You need to plan how far your materials will go. Longer trips need stronger airflow and bigger machines. You should look at your building's layout. Sharp turns and small spaces can slow things down or wear out parts. You can use bendy pipes to fit your space, but try to keep the path straight for best results.
Flow Rate and Capacity
You must know how much you want to move each hour. Flow rate and system size change the equipment you need. If you want to move a lot faster, you need bigger blowers and wider pipes. You should measure what you need before you buy or upgrade.
Energy and Cost
You want a system that saves energy and costs less. Pneumatic Conveying Equipment uses smart blowers and special drives to use less power. Smart air control helps you save energy. The table below compares pneumatic and mechanical systems:
Attribute | Pneumatic Conveying Systems | Mechanical Conveying Systems |
|---|---|---|
Energy Efficiency | Uses less energy | Uses more energy |
Maintenance Needs | Needs less fixing | Needs more fixing |
Flexibility | Very flexible | Not as flexible |
New pneumatic systems are simple. You spend less on repairs and downtime. You can add these systems to what you have without much trouble.
Safety and Compliance
You must keep workers and products safe. Pick equipment that meets safety rules and laws. Dusty materials need closed systems to keep air clean. You should check for safety labels and follow local rules. This keeps your building safe and stops fines.
Tip: Think about your needs for material, distance, flow, energy, and safety before you pick your system. Good planning helps you get the best results.
Operation and Maintenance Tips
Routine Maintenance
You keep your pneumatic conveying equipment working well with a good plan. Start by checking your system often. Look at it every day, week, and month to find problems early. Clean out any dirt from the machines. Change old or broken parts. Put oil on moving parts to stop them from wearing out. Always check how much your system is carrying. Do not put too much in at once. Clean your equipment a lot to help it work better and spot problems. Teach your workers how to use the equipment safely. Make sure everyone follows safety rules and wears safety gear. Use special systems to watch how your equipment works all the time. Test how much your system can carry and check safety often. Write down all the work you do on your equipment. This helps you plan and follow safety rules.
Routine Maintenance Checklist:
- Check your system often.
- Clean and change old parts.
- Oil moving parts.
- Watch how much you carry.
- Keep things clean.
- Teach workers' safety.
- Follow safety rules.
- Use systems to watch equipment.
- Test and check safety.
- Write down all work.
Troubleshooting
You fix problems faster when you know what to look for. If your system slows down or stops, look for things blocking pipes or feeders. Listen for weird sounds from blowers or compressors. Check valves and airlocks for leaks. Look for dust around receivers and separators. If materials move unevenly, check for broken parts or loose connections. Use data from your system to find drops in how well it works. Fix small problems before they get worse.
Tip: Always fix strange sounds, leaks, or dust right away. Acting fast stops big repairs.
System Optimization
You make your system better by changing small things. Change airflow and pressure to fit your material. Get blowers and compressors that use less energy. Use smart controls to watch and change flow rates. Look at your system layout and remove sharp bends in pipes. Teach your team the best ways to work. Check how your system works often and update your plan. These steps help you save energy, stop breakdowns, and make your equipment last longer.
Optimization Step | Benefit |
|---|---|
Change airflow/pressure | Materials move better |
Get better equipment | Use less energy |
Use smart controls | Watch the system in real time |
Fix layout | Fewer blockages |
Teach your team | Safer work |
You keep your pneumatic conveying system working well by focusing on maintenance, fixing problems, and making improvements.
Common Misconceptions
Myths vs. Facts
You may hear many things about pneumatic conveying equipment that are not true. Some myths can lead you to make poor choices or overlook important details. Here are common myths and the real facts:
Myth | Fact |
|---|---|
Pneumatic systems only work for light materials. | You can move heavy, abrasive, or fragile materials with the right system. |
These systems always create dust and mess. | Modern designs keep materials sealed and reduce dust. |
You must spend a lot on maintenance. | Routine checks and good design lower maintenance costs. |
All systems use too much energy. | New blowers and smart controls help you save energy. |
You cannot use pneumatic conveying in small spaces. | You can fit these systems into tight layouts with flexible piping. |
Note: You should always check the facts before you choose equipment. Ask experts and read technical guides to avoid mistakes.
Mistakes to Avoid
You want your pneumatic conveying system to work well and last long. Avoid these common mistakes:
- Ignoring Material Properties: You must match your system to the material. If you skip this step, you may face clogs or damage.
- Poor System Layout: Sharp bends and long routes slow down flow and wear out parts. Plan a straight and simple path.
- Skipping Routine Maintenance: If you do not check your system often, small problems can grow and cause breakdowns.
- Choosing the Wrong Blower: You need the right blower for your material and flow rate. A mismatch leads to wasted energy and poor performance.
- Overloading the System: Too much material at once can block pipes and damage equipment. Always follow the recommended capacity.
Tip: You should work with trusted suppliers and follow best practices. This helps you avoid costly errors and keeps your system running smoothly.
You now know what pneumatic conveying equipment does. You learned how it moves materials with air. You found out about the main parts and types of systems. You also learned what to think about when picking equipment. You know how to keep your system working well.
Remember: Picking the right design and equipment keeps things safe. It helps you move materials easily and quickly. Use this guide to make good choices. Keep learning as your needs change.
FAQ
What materials can you move with pneumatic conveying equipment?
You can move powders, granules, and pellets. Small bulk solids also work in these systems. Many industries use them for food and chemicals. Cement and pharmaceuticals use them too. You need to match the system to your material. This helps you get the best results.
How do you choose between dilute and dense phase conveying?
Pick a dilute phase for light materials that flow easily. Use dense phase for fragile or rough products. Always think about your material's size and shape. Check how easily it breaks before you choose.
How often should you perform maintenance on your system?
Check your system every day. Do deeper inspections once a month. Clean parts and replace worn items often. Watch airflow to spot problems early. Routine maintenance stops breakdowns and keeps equipment safe.
Can you upgrade an existing system to improve efficiency?
You can upgrade blowers and controls. You can also change the piping for better flow. Smart sensors help save energy and lower downtime. Always talk to experts before you make changes.
How to Choose a High-Speed Mixer
Learn how to choose the right high-speed mixer for your production line.Compare types,materials,and features to find the best industrial mixer for your needs.
Top Tips for Choosing the Ideal SRL-Z Series Vertical Mixing Unit
Discover the SRL-Z Series Vertical Mixing Unit—high-speed mixing,consistent uniformity,automation,energy efficiency,and optimal space use.Learn features,applications,maintenance tips,and how to choose the right model for your factory.
The Core Advantages of Audop PVC Automatic Weighting and Conveying System
Discover the core advantages of the Audop PVC Automatic Weighting and Conveying System.Learn how accurate weighing,dust-free conveying,smart automation,and modular design help you improve PVC production efficiency and stability.
Recycle Smarter: 5 Trends of Plastic Waste Recycling Machines
Discover the top 5 trends shaping modern plastic waste recycling machines-from smart automation to energy-efficient pelletizing.Learn how advanced solutions like the Audop Plastic Recycling Machine improve efficiency,flexibility,and sustainability.
How to Operate the Pipe Chain Conveyor More Effectively and the Methods for Handling Faults
Learn practical ways to operate the pipe chain conveyor more efficiently,reduce downtime, and handle common faults with ease.Discover expert tips and reliable equipment like the Audop Pipe Chain Conveyor for better material handling performance.